Table of Contents
Introduction
Art is never finished, only abandoned. — Leonardo da Vinci
This project aims to develop and identify the best Deep Learning (DL) model for classifying paintings based on their artistic movement (e.g., Renaissance, Impressionism, Realism). The classification requires detecting subtle details, making the depth of neural network layers and the number of parameters crucial for success. The motivation behind this project is to create a mobile application that can assist users in identifying the artistic style of a painting by simply taking a photograph of it. This could be especially useful in museums or for students of art history.
Analysis of the Dataset
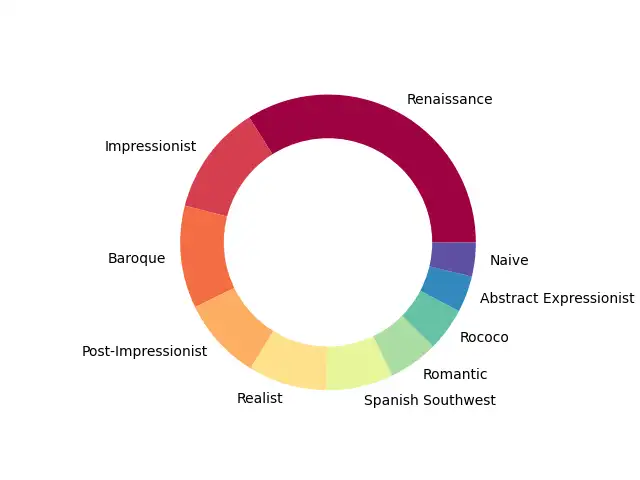
The dataset used is from the National Gallery of Art in Washington, D.C., chosen for its extensive collection and detailed metadata. The dataset was filtered to include only paintings and prints, classified into the top 10 artistic styles, resulting in 7,977 images. The use of a well-documented and open-access database ensures the reliability and reproducibility of the project.
Study of the Database and Data Acquisition
A thorough understanding of the entity-relationship model of the database was essential for selecting the relevant tables and fields. The central table ‘objects’ contains information on all listed artworks, while other tables provide additional metadata such as image links and classification terms. By understanding this model, we could effectively query and extract the necessary data for our project.
Data Filtering and Cleaning
The dataset was filtered to retain only paintings and prints, reducing the total from 140,240 objects to 70,040. Further filtering to include only the top 10 artistic styles resulted in a final dataset of 7,977 images. This step involved removing irrelevant objects and ensuring that only those with sufficient metadata and images were included, thus enhancing the quality of the training data.
Image Acquisition
A Python script was used to download the images and organize them into folders corresponding to their artistic style. This automated process involved creating directories for each style and downloading images directly from the provided URLs, ensuring a systematic and efficient organization of the dataset for model training.
Final Data Validation
An expert in art history validated the final dataset to ensure accuracy. This involved reviewing random samples from each artistic style to confirm that the classification provided by the museum was correct. This step was crucial to ensure the reliability of the training and validation sets.
Data Preparation
The dataset was split into training and validation sets using a stratified approach to ensure balanced representation of each artistic style. This method ensured that each subset of data accurately reflected the distribution of styles in the overall dataset, which is critical for training robust and generalizable models.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
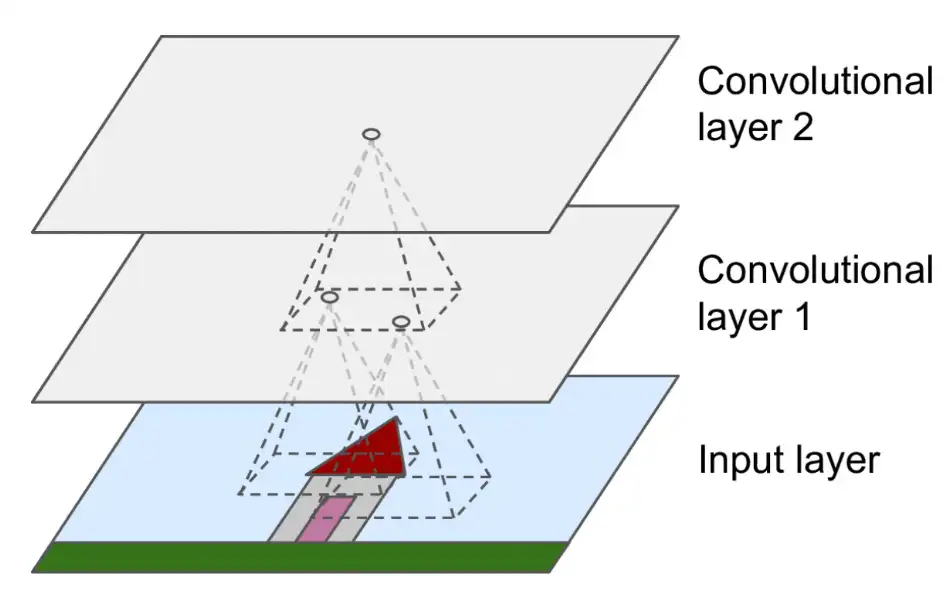
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are a class of deep learning models particularly effective for image classification tasks. They are inspired by the visual processing mechanisms of the human brain and consist of multiple layers that automatically and adaptively learn spatial hierarchies of features from input images.
Key Components of CNNs
- Convolutional Layers: These layers apply convolution operations to the input image, using filters (or kernels) that slide over the image to detect various features such as edges, textures, and patterns.
- Pooling Layers: Typically used after convolutional layers, pooling layers reduce the spatial dimensions of the feature maps, thereby reducing the number of parameters and computational load.
- Fully Connected Layers: These layers are similar to traditional neural networks and are used to perform the final classification based on the features extracted by the convolutional and pooling layers.
- Activation Functions: Functions like ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) introduce non-linearity to the model, enabling it to learn complex patterns.
- Dropout Layers: Used to prevent overfitting by randomly setting a fraction of input units to zero during training.
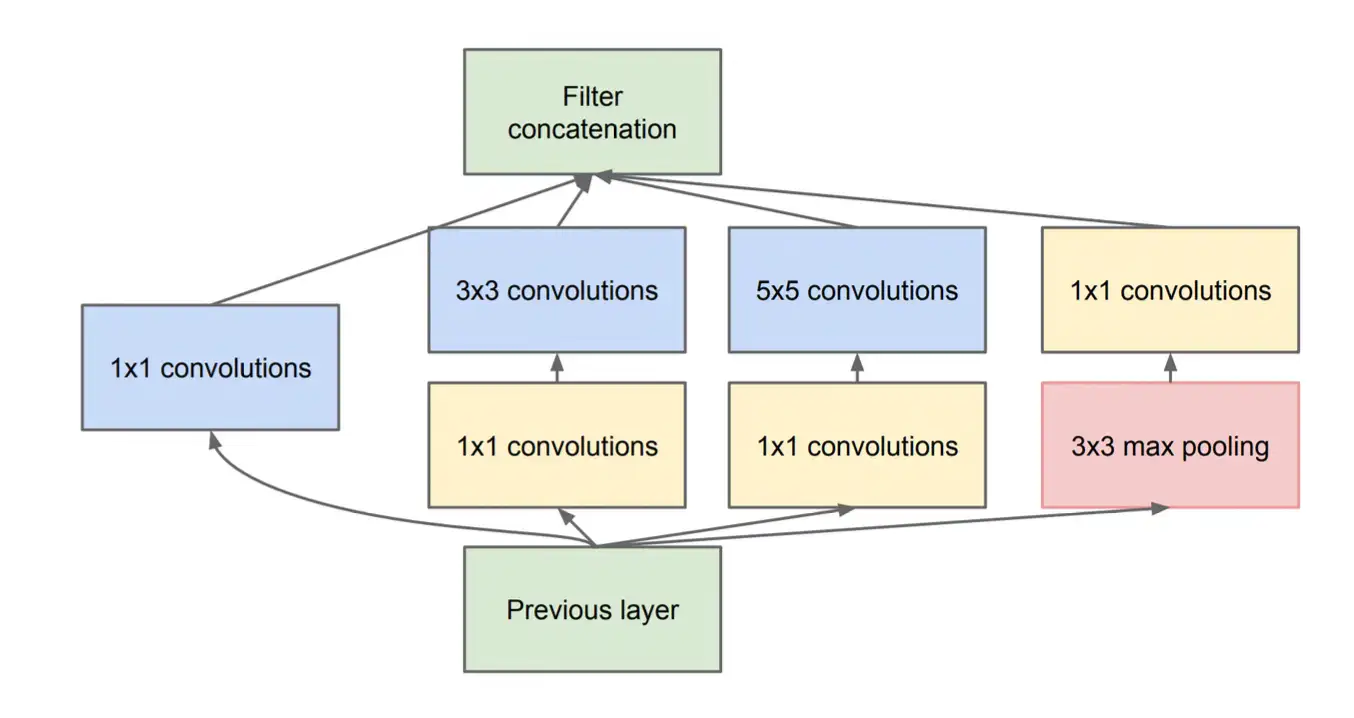
CNN Models
We constructed a series of CNN models, each with varying complexity and regularization techniques, to evaluate their effectiveness in classifying paintings based on their artistic movement. Some of the architectures included:
- Standard Model without Regularization
- With Regularization and More Filters
- Data Augmentation
- Inception
- EfficientNet
Conclusions
The EfficientNet-based model was the most successful, highlighting the effectiveness of transfer learning and pre-trained models. However, the overall accuracy suggests that further improvements are possible, potentially through expanding the dataset.
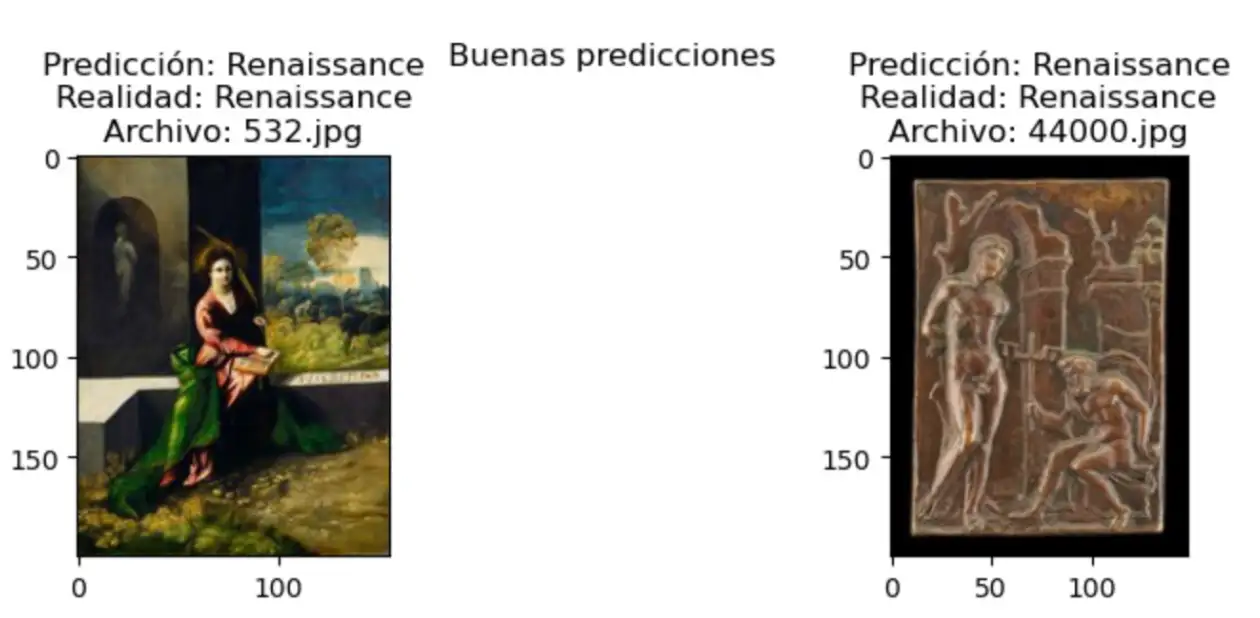

Here you can find the extended analysis, including the results of the cross-validation and the comparison of the models.
